01 definition of landslide Speaking of landslides, you may not be strangers. Whenever the rainy season comes, there will be reports on landslides on TV every three, and the scale will be large or small, sometimes hurting people's lives. How is landslide generated? Most of the pictures on landslides on TV have the following characteristics: mountainous areas, landslides are loose, rainy or raining. In fact, this has already told us a few key factors for the occurrence of landslides. The landslide is essentially a gravity flow, that is, the material flows from high to low under the action of its own gravity, so the landslide occurs mostly in high and low undulating mountains and hills. In addition, the mountain body needs to be loose, that is, there are some soft surfaces that are easy to slide inside. These soft surfaces may be the original layer of the rock layer, or may be the fracture surface generated during geological movement, and long-term weathering (such as water infiltration) It produces a weathered surface that is easy to slide. After satisfying the foregoing conditions, sometimes there are some predisposing factors. Rainfall is the most common type—water is equivalent to a lubricant, but the adhesion inside the mountain is less than the sliding force generated by gravity, which induces landslides. In addition, earthquakes, snowfall, volcanoes, etc. can also induce landslides. In recent years, human activity has become an important incentive for the transformation of the mountain irrational, unplanned digging coal mining and so can induce landslides. The generalized landslide can be divided into several types according to the material composition of the landslide body and the difference of the sliding process. The composition of the landslide body can be earthy, can be rock fragments, or even huge rock masses. The movement of the landslide body is also very different. It can be rapid collapse, flow, speed of hundreds of kilometers per hour, or slow creep, making it almost impossible to feel the movement of the landslide body. Type of landslide (picture from USGS) 02 landslide hazards Landslides generally cause large or small disasters, and the more people there are, the greater the loss. In May 2014, landslides in Afghanistan were estimated to have killed 300 to 600 people. The landslide occurred in the remote Padhhashan province of Afghanistan, in the Pamirs. Here, like the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, due to the collision of the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate, the geological movement is active and the earthquake is frequent. The mountain is severely weathered and fragmented under the influence of rainfall. Moreover, during the week before the landslide occurred, there was a once-in-a-century heavy rainfall. The rainfall caused the soil to nearly saturate, the mountain was overwhelmed, and eventually slipped down to bury the nearby village. Aerial photography of the landslide in Afghanistan. (Image courtesy of theatlantic.com) Water: the accomplice of the landslide The danger of landslides to humans is not limited to direct burial such as the landslide in Afghanistan. In many cases, it will have an accomplice: water. In 1963, a huge landslide occurred in the Vaughan Reservoir in Italy. About 0.25 cubic kilometers of rock mass slid into the reservoir at a speed of 110 kilometers per hour, which ignited a huge wave about 250 meters high. The huge waves quickly rushed downstream, causing many villages and cities to be destroyed, killing approximately 2,500 people. The reservoir is the cause of the huge landslide, and the landslide body rushes into the reservoir and induces large-scale floods. This is a painful lesson, but the dam is quite strong and not bad. The Vaian dam, still standing for decades. (Image courtesy of dmctrentino.it) Earthquake, demon accompanied by landslides Landslides are often accompanied by another daunting natural disaster, which is an earthquake. Earthquakes that occur in the hilly terrain of the mountains are bound to cause landslides, and the damage it causes is sometimes no less than the earthquake. The US Geological Survey (USGS) listed 25 large landslide events in the 20th century, up to 9 earthquake-induced, the highest proportion of all incentives. During the Wenchuan earthquake, Beichuan County was buried, and countless people were sleeping under the landslide. Since the earthquake, there have been frequent landslides, constantly rushing roads and blocking tunnels. Landslides and mudslides rushed into the river, and some of the rivers that flowed through the disaster area were lifted by one or twenty meters. It is already approaching the Dujiangyan-Wenchuan Expressway. Large-scale landslide caused by the Wenchuan earthquake Barge Lake, a dangerous source of secondary disasters Earthquake landslides may also block rivers and form barrier lakes. The second disaster may be more serious after the dam breaks. After the Wenchuan earthquake, reports on the barrier lake repeatedly appeared on television. Due to proper response, the Wenchuan earthquake did not cause much damage. However, historically, the damage caused by the barrier lake may be greater than the damage caused by the earthquake and the landslide itself. In 1933, a 7.5-magnitude earthquake struck Maoxian County, Sichuan Province, called the Diexi Earthquake. The earthquake caused about half of the area of ​​the ancient town of Diexi to slide into the Minjiang River. At the same time, it caused many large landslides, blocking the Lancang River and some tributaries, forming a number of dammed lakes, one of which just flooded the collapsed ancient town of Diexi. Then these barrier lakes overflowed the dam one after another. More than a month later, under the trigger of a strong aftershock, these dammed lakes eventually dammed. At that time, at the time of the night, the water head of more than 70 meters rushed down, swallowed Maoxian and Wenchuan, arrived at Dujiangyan in the middle of the night, and caused great losses to Wenjiang, Chengdu and other places in the Chengdu Plain. It is said that the floods destroyed dozens of villages and drowned thousands of people. In Dujiangyan, only 4,000 bodies were recovered. Another way of saying it is that more than 20,000 people have drowned. In the following decades, there have been many dam breaks and submerged downstream. At present, Maoxian retains several barrier lakes, but they are all well monitored and governed. In the village of Diexi, you can see a dammed lake from the Diexi earthquake. This landscape is named “Soul Turtle Tourâ€. In 1786, a major earthquake occurred in Kangding, Sichuan, and the landslide blocked the Dadu River and formed a barrier lake. After only 9 days, the dam broke out in the dam, the flood rushed down, flooded a large number of towns and villages, and the number of drowning people was countless. Yichang did not stop until thousands of miles later, but the number of people directly killed in the earthquake was more than 400. In Kyrgyzstan, the magnitude 7.4 earthquake of 1911 induced the second major landslide, forming a dammed lake with a height of 600 meters. It is the largest existing dam - the Three Gorges Dam is only 185 meters high. The dam site is located on the Pamirs above 3,000 meters above sea level and is still a major problem hanging on the heads of the lower reaches. Where does the biggest landslide occur? On May 18, 1980, before the eruption of the St. Lawrence volcano in Washington State, a 5.1 volcanic earthquake induced a landslide. The volcanic eruption then pushed the debris of the mountain collapse and the volcanic debris to continue to slide, and the landslide body moved at a high speed. At 177-249 km/h, it glided over a lake, crossed a 350-meter-high ridge about 10 km north, and finally stayed in a river 21 km away, filling the valley about 180 meters. The volume of the landslide body is approximately 2.8 cubic kilometers, which is the largest landslide event on land ever. The scene after the eruption of St. Helens (the lens is north). The small image on the left was taken on a lake in the northern part of the volcano before the eruption, and the small picture on the right was taken at about the same position after the volcanic eruption. The landslide and the subsequent explosion of the crater made the volcano look like today. (Image courtesy of wiki commons) Of course, landslides can occur not only on land, but also under water. About 8,000 years ago, in the western part of Norway, about 100 kilometers from the coast, a huge landslide occurred, and the volume of the landslide was about 3,500 cubic kilometers. This is currently the largest known landslide on the planet, equivalent to 1,250 times the St. Lawrence landslide. The landslide induced a huge tsunami. When it reached the Norwegian coast, the waves reached 10 meters. When it reached the northern coast of Britain, the wave height was still about 3 meters. Is the landslide only a disaster? The landslide will undoubtedly bring a painful disaster to the people in the world, taking away life and flooding the homeland. But sometimes, the landslide pair will also bring some benefits to future generations. The landslide forms a dammed lake, which can add a lot to the gorge and form a beautiful scenic spot. For example, after the Diexi earthquake, a unique group of barrier lakes was formed, many of which have remained to this day, dotted with canyons, and become a beautiful Songpinggou scenic spot. New Zealand's Waikaremoana Lake was formed after a major earthquake-induced landslide in the 19th century and is now a tourist attraction in New Zealand. In addition to good-looking, the barrier lake can still be used? Power generation! The barrier lake generally occurs in the canyon area, often with a relatively large height difference, which is an ideal place for the construction of hydropower stations - the above mentioned Huaikaemoa Nahu Lake has been building hydropower stations since the 1940s. Ba Songsuo in the Linzhi area of ​​Tibet is also a barrier lake. It is not only beautiful in scenery, but also people build channels from the dam body of the dammed lake to divert water to the power station 10 kilometers downstream. This measure can meet the needs of surrounding towns and villages. Electricity demand. The beautiful Bashon is wrong. (Image courtesy of wiki commons) 03 How to prevent and predict the occurrence of landslides? Because landslides are extremely harmful and frequent, research on prevention and prediction of landslides has always been a hot topic in engineering. In the field of practical engineering, it is possible to set up a landslide body by setting a stone wall (net), slope protection, anti-slide pile, etc., to build a tunnel, bridge, etc. to avoid the landslide body, or to directly reduce or cut the landslide body and directly exclude the landslide harm. For residential sites and important engineering projects, the best way is to stay away from landslides. Another difficulty in landslide mitigation is the detection and prediction of large landslides with greater threats. Many densely populated towns are just built on landslides or within the threat of landslides. Some reservoirs also have high-risk landslides in the reservoir area. Once they slide, the losses are huge. Generally, we can determine the position of the landslide body by means of satellite imagery or aerial interpretation, field investigation, exploration and other methods. For landslides with huge threats, a monitoring network should be established and closely monitored. Some theories suggest that landslide movement generally experiences three stages of slow sliding, stable sliding, and accelerated sliding, and instability occurs after accelerated sliding, resulting in catastrophic landslides. In 1985, a huge landslide occurred in Zigui, Hubei, which destroyed the ancient town of Xintan. However, due to the early and strict monitoring, the landslide was predicted in advance, and the masses were evacuated in time. There were no casualties in 1,371 people in the sliding area. Scholars at home and abroad have also proposed many theoretical models to try to solve the problem of landslide prediction. However, although there are many cases of successful predictions, landslide prediction is still a worldwide problem. When landslides are destroyed, landslide research still has a long way to go.
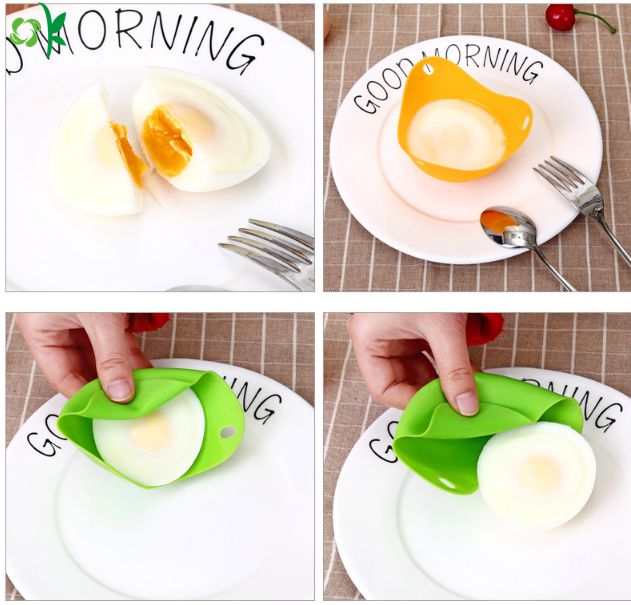
About silicone egg products:
Multi-Function:
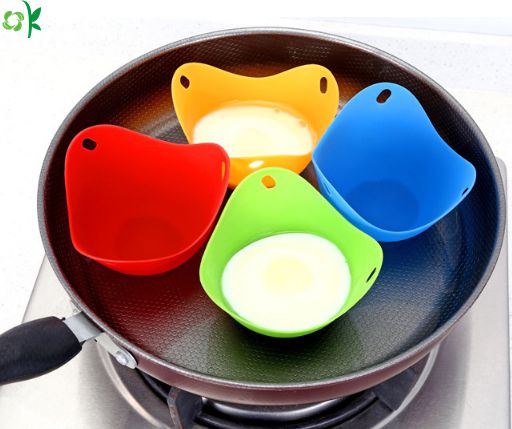
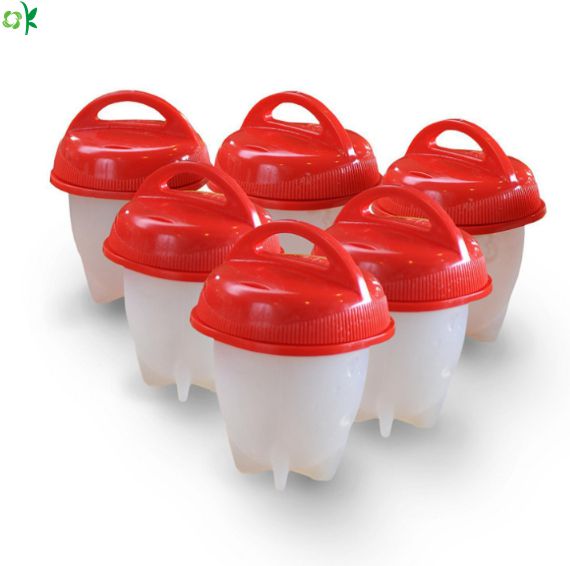
Easy and convenient to cook soft, medium or hard-boiled eggs
Great for cooking eggs bites, egg white, fruit, cupcakes, frozen treats, candy
Perfect holder for sorting small items. Fun for a birthday or holiday party, baby shower, picnic, wedding or showcase.
Easy To Use & Clean:
Hard lid with a screw and allows for convenient adding flavor etc.
Dishwasher safe without harsh detergents,
Silicone Egg Poacher Details:
1.Product name:
10.Silicone egg products photos for reference.
Silicone egg poacher,silicone egg boil,silicone egg container,Silicone Egg Cooker Dongguan OK Silicone Gift Co., Ltd. , https://www.dgsiliconebabyproducts.com







2.Place of origin:Guangdong China
3.Color:any pantone color can be done
4.Logo:printed,debossed,embossed
5.MOQ:500pcs,special design can be flexible .
6.Package:1 pcs/opp,customized design is available.
7.Design:Customized
8.Certification:FDA,LFGB,SGS,ROHS,etc.
9.Compatible Brand:for all egg product



Causes, hazards and predictions of landslides
How does landslide harm life and property?